Cache Group Operator
Enterprise users can use the Cache Group Operator to create and manage distributed cache clusters. Compared to other deployment methods, the Cache Group Operator is more convenient to use (supporting both GUI and CLI) and also supports advanced features such as different node configurations, smooth scaling, and automatic cache cleaning.
Install the Cache Group Operator
Install Helm and add the JuiceFS Helm chart repository:
helm repo add juicefs https://juicedata.github.io/charts/
helm repo update
Before installation, read values.yaml to learn all available configuration items. If modifications are needed, create a new values file (for example, values-mycluster.yaml) and include the parts you want to modify. If you need to install the operator on multiple Kubernetes clusters, create separate values files for each cluster configuration.
# Modify values-mycluster.yaml as needed
helm upgrade --install juicefs-cache-group-operator juicefs/juicefs-cache-group-operator -n juicefs-cache-group --create-namespace -f values-mycluster.yaml
You can use kubectl wait to wait until the operator is ready:
kubectl wait -n juicefs-cache-group --for=condition=Available=true --timeout=120s deployment/juicefs-cache-group-operator
Once the Cache Group Operator is installed, you can start creating and managing cache groups. The operations introduced in the following sections can be completed through both the CSI Dashboard (version 0.25.3 or above) and kubectl. Choose the method you prefer. To simplify the documentation examples, only the kubectl method will be introduced.
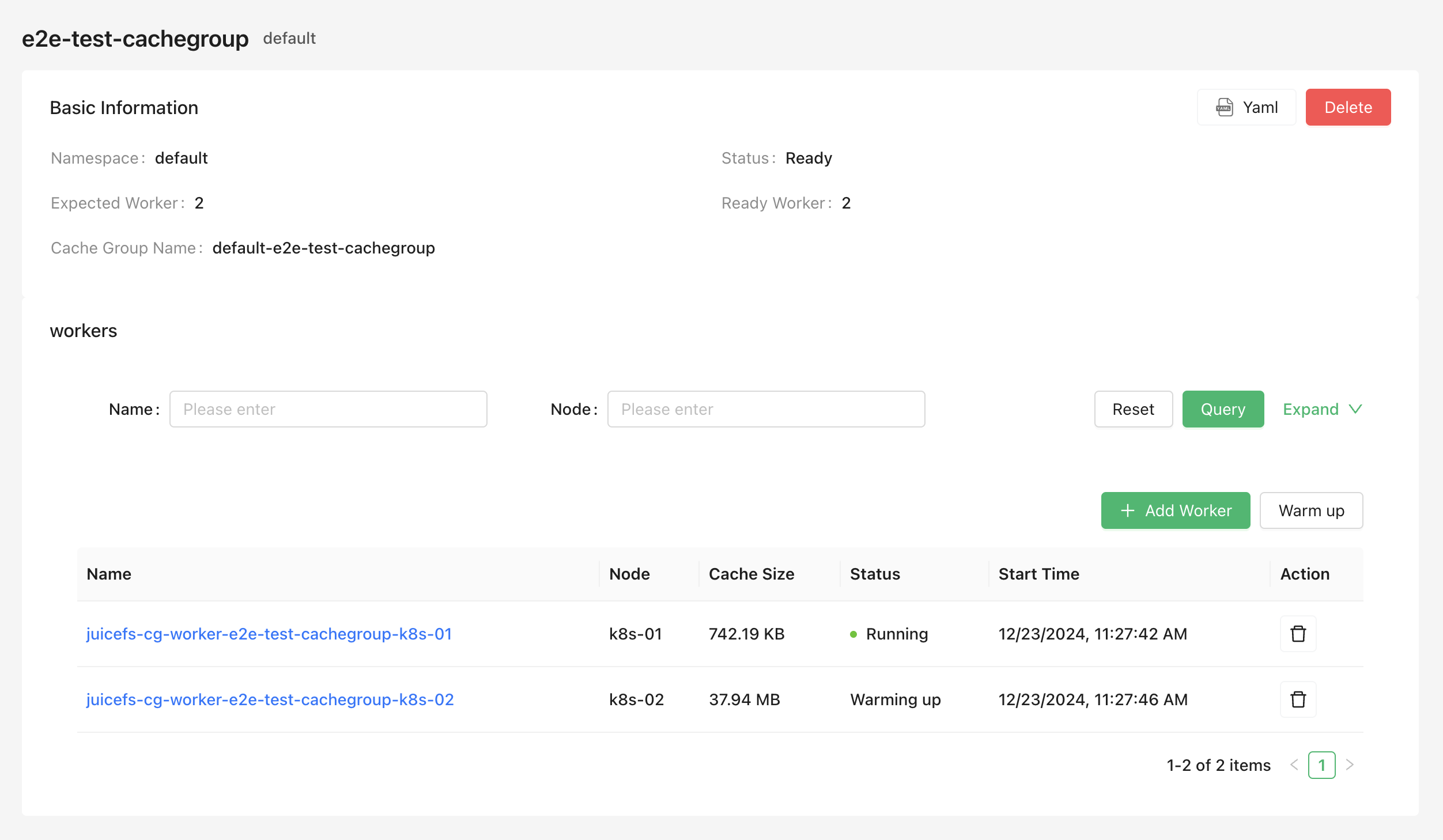
Create a cache group
Refer to the following example to save the cache group configuration as a YAML file (for example, juicefs-cache-group.yaml). This example deploys a distributed cache on all nodes with the juicefs.io/cg-worker: "true" label (you can set any label you like). For more configuration options, refer to the Cache group configurations section.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: juicefs-secret
namespace: juicefs-cache-group
type: Opaque
stringData:
name: juicefs-xx
token: xx
access-key: xx
secret-key: xx
---
apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
spec:
secretRef:
name: juicefs-secret
worker:
template:
nodeSelector:
juicefs.io/cg-worker: "true"
image: juicedata/mount:ee-5.1.1-1faf43b
opts:
- cache-size=204800
- free-space-ratio=0.01
- group-weight=100
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
memory: 128Mi
limits:
cpu: 1
memory: 1Gi
Then create the cache group using the kubectl apply command:
kubectl apply -f juicefs-cache-group.yaml
If the Kubernetes nodes do not have the juicefs.io/cg-worker: "true" label, add this label:
kubectl label node node1 juicefs.io/cg-worker=true
Check cache group status
Use the following command to check the cache group status and confirm that the cache group is in the "Ready" state:
$ kubectl get cachegroups
NAME CACHE GROUP NAME PHASE READY AGE
cachegroup-sample juicefs-cache-group-cachegroup-sample Ready 1/1 10s
Use the cache group
After completing the above steps, a JuiceFS distributed cache cluster has been started in Kubernetes, with the cache group name juicefs-cache-group-cachegroup-sample. To allow the JuiceFS client of the application to use this cache cluster, the JuiceFS client needs to join this cache group and add the --no-sharing mount option. This way, the JuiceFS client of the application joins the cache group but does not participate in cache data construction, avoiding cache data instability caused by frequent client creation and destruction.
For dynamic configuration, modify the mount options as shown below. For more information on how to adjust mount configurations, see Mount options.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: juicefs-sc
mountOptions:
- cache-group=juicefs-cache-group-cachegroup-sample
- no-sharing
Add and delete cache nodes
The Cache Group Operator supports smooth scaling of cache nodes, ensuring that adjustments do not significantly impact cache hit rates.
In the Create a cache group example, Kubernetes nodes must have the juicefs.io/cg-worker: "true" label. Therefore, adding or deleting cache nodes involves adding or removing this label from Kubernetes nodes. For example, use the kubectl command to add or delete nodes:
# Add nodes
kubectl label node node1 juicefs.io/cg-worker=true
kubectl label node node2 juicefs.io/cg-worker=true
# Delete nodes
kubectl label node node1 juicefs.io/cg-worker-
When nodes change, the Cache Group Operator will smoothly add or delete nodes. The specific logic is as follows:
-
When adding nodes, the Cache Group Operator automatically creates new Worker Pods and adds the
group-backupmount option. If the new Worker Pod receives an application request and finds a cache miss, it forwards the request to other cache nodes to ensure cache hits. By default, thegroup-backupmount option will be removed after 10 minutes, which can be controlled by thespec.backupDurationfield:apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
spec:
backupDuration: 10m -
When removing nodes, the Cache Group Operator first attempts to migrate the cache data on the node to other nodes before deleting the node. The maximum waiting time is 1 hour by default, which can be controlled by the
spec.waitingDeletedMaxDurationfield:apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
spec:
waitingDeletedMaxDuration: 1h
Warmup Cache Group
Operator supports creating a WarmUp CR to warmup the cache group.
apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: WarmUp
metadata:
name: warmup-sample
spec:
cacheGroupName: cachegroup-sample
# The default strategy is Once, meaning it run only once.
# The following examples are scheduled to run every 5 minutes.
policy:
type: Cron
cron:
schedule: "*/5 * * * *"
# if empty, the default is to warmup the entire file system.
targets:
- /a
- /b
- /c
# warmup options
# ref https://juicefs.com/docs/cloud/reference/command_reference/#warmup
options:
- threads=50
Cache group configurations
All supported cache group configurations can be found in the complete example.
Update strategy
When updating the cache group configuration, you can specify the update strategy for the worker nodes under the cache group using the spec.updateStrategy field.
Currently supported strategies are:
RollingUpdate(default): This is the default update strategy. When using theRollingUpdatestrategy, after updating the cache group template, the old Worker Pods will be terminated, and new Worker Pods will be automatically created. The number of updates at a time follows thespec.updateStrategy.rollingUpdate.maxUnavailableconfiguration, which defaults to 1.OnDelete: When using theOnDeletestrategy, after updating the cache group template, new Worker Pods will only be created when you manually delete the old Worker Pods.
apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
spec:
updateStrategy:
type: RollingUpdate
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
Cache directory
The cache directory can be set using the spec.worker.template.cacheDirs field. Supported types are HostPath and PVC.
apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
namespace: default
spec:
worker:
template:
nodeSelector:
juicefs.io/cg-worker: "true"
image: juicedata/mount:ee-5.1.1-1faf43b
cacheDirs:
- type: HostPath
path: /var/jfsCache-0
- type: PVC
name: juicefs-cache-pvc
Specify different configurations for different nodes
Cache nodes may have heterogeneous configurations (for example, different cache disk sizes). In this case, you can specify different configurations for different nodes using the spec.worker.overwrite field:
apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
spec:
worker:
template:
nodeSelector:
juicefs.io/cg-worker: "true"
image: juicedata/mount:ee-5.1.1-1faf43b
hostNetwork: true
cacheDirs:
- path: /var/jfsCache-0
type: HostPath
opts:
- group-weight=100
overwrite:
- nodes:
- k8s-03
# You can also use nodeSelector
# nodeSelector:
# kubernetes.io/hostname: k8s-02
opts:
- group-weight=50
cacheDirs:
- path: /var/jfsCache-1
type: HostPath
- path: /var/jfsCache-2
type: HostPath
Mount options
Mount options can be set using the spec.worker.template.opts field. Refer to the documentation for all mount options.
apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
namespace: default
spec:
worker:
template:
nodeSelector:
juicefs.io/cg-worker: "true"
image: juicedata/mount:ee-5.1.1-1faf43b
opts:
- group-weight=100
Cache group name
The Cache Group Operator generates default cache group names in the
${NAMESPACE}-${NAME} format. If you want to customize the cache group name, you can set it using the spec.cacheGroup field:
apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
spec:
cacheGroup: jfscachegroup
Clean cache when deleting a node
When deleting a node, you can specify whether to clean the cache using the spec.cleanCache field:
apiVersion: juicefs.io/v1
kind: CacheGroup
metadata:
name: cachegroup-sample
spec:
cleanCache: true
Delete a cache group
Use the following command to delete the cache group. All worker nodes under the cache cluster will be deleted:
kubectl delete cachegroup cachegroup-sample

